背景 近期需要在OpenShift集群中部署Nginx服务做为负载均衡器,负载集群外部服务,如NTP、DNS、项目App等。因为不同的服务的配置都是不一样的,不仅后台服务的IP不一样,而且使用的协议也不一样,HTTP/TCP/UDP都有可能,如果按照传统的方式来实施的话,每一个应用单独定义Nginx配置,分别部署,每增加一个新的应用被负载都需要做一次复杂的过程,那么有没有办法能够让这过程变得简单呢,甚至能够自动化处理,我们只需要提供最简单的信息?
打包方案选择 1. Template 对于OpenShift熟悉的朋友,会马上想到使用Template模板来实现。
不足之处:
OpenShift特有,如果是使用OpenShift容器平台的话,这个不足可忽略。
无法保证线上资源状态始终与参数设定的结果一致,如手动增加rc的副本数时,不会自动恢复到与参数设定的副本数。
在创建的时候设置参数,如果在应用运行时对参数动态更新的话,则需要使用脚本命令使用所有的参数,重新生成资源列表。参数需要额外管理,不可靠。
如果应用有创建的顺序有依赖,则无法满足。
无法根据参数的不同对资源进行条件控制。
2. Helm 对于Kubernetes熟悉的朋友,会马上想到使用Helm来实现。
不足之处:
需要额外部署Helm客户端及Tiller。
需要额外管理helm中的charts资源。
无法保证线上资源状态始终与参数设定的结果一致。
如果应用有创建的顺序有依赖,则无法满足。
参数更新时,需要手动执行helm脚本
3. 创建Ansible playbook 对于熟悉各种自动化工具的运维开发,会想到使用自动化配置管理工具来做,如ansible。
不足之处:
需要额外部署Ansible,及对ansible访问集群的访问认证。
需要额外管理ansible的playbook文件。
无法保证线上资源状态始终与参数设定的结果一致。
参数更新时,需要手动执行ansible playbook脚本
4. operator Operator即为今天的主角,我将给予更加详细的介绍。
go类型,它的实现更加灵活,可以随心所欲,扩展性也最强,构建出的operator镜像也不大,但是它对于编程能力要求高,同时没有ansible和helm类型拿来即用,可读性也不及ansible与helm类型。
ansible类型,它使用ansible的playbook方式来定义应用的构建与保证应用的状态,它的实现也很灵活,依赖于ansible的模块,但是这使得构建出的operator镜像较大,一般为600多M,因为它包含了ansible应用及默认的各个模块。
helm类型,它使用helm的charts方式来定义应用的构建与保证应用的状态,它的镜像一般为200多M,但是它的灵活度不及另外两种类型。
一般情况下,以上三种方式都能够满足要求,建议大家使用自己最熟悉的方式。构建方式并不是我们的约束点,我们最关心的是能够部署按要求的应用,并保证应用一直处于稳定的状态。
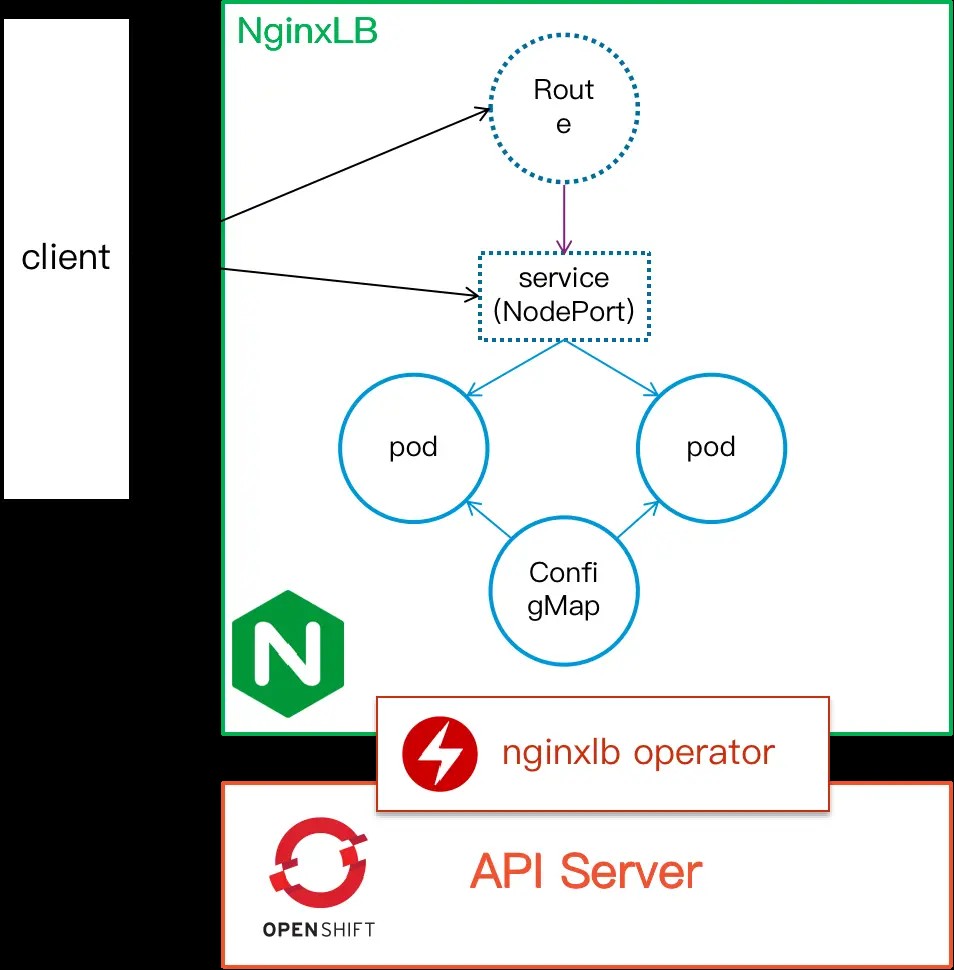
构建分析 1. 资源类型
deployment,运行Nginx应用
service,运行Nginx service
configmap,设置Nginx负载均衡上游及协议类型等配置
route,对于HTTP协议可以设置指定的域名
NginxLB,添加的CRD资源对象名
2. 参数设置
nginx_image, 指定Nginx应用镜像
size,Nginx应用运行的副本数
loadbalancers,设定的负载均衡参数配置列表
loadbalancers[].protocol,负载均衡网络协议,支持HTTP/TCP/UDP
loadbalancers[].port,负载均衡Nginx监听的端口
loadbalancers[].nodeport,如果负载均衡使用nodeport方式对外提供服务,则可以用该参数指定nodeport端口号
loadbalancers[].upstreams,负载均衡上游服务列表
loadbalancers[].hostname,对于HTTP协议,可以指定hostname来创建OpenShift Route资源
最终需要实现的NginxLB资源的参数例子为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 apiVersion: fcloudy.com/v1alpha1 kind: NginxLB metadata: name: example-nginxlb spec: nginx_image: "docker.io/xhuaustc/nginx:alpine" size: 2 loadbalancers: - protocol: TCP port: 53 nodeport: 32287 upstreams: - 192.168.4.5:53 - 192.168.5.3:53 - protocol: HTTP port: 80 upstreams: - 192.168.4.5:80 hostname: xx.nginx.fcloudy.com
以下为NginxLB Operator相关资源的关系
3. Operator类型
选择ansible类型,使用它的主要是与集群运维及自动化运维等技术栈统一。
制作Operator 通用步骤与说明可以参考OpenShift 通过Operator SDK制作Operator ,本案例的具体操作如下
新建一个operator项目(type=ansible 资源类型为NginxLB)
1 $ operator-sdk new nginxlb-operator --api-version=fcloudy.com/v1alpha1 --kind=NginxLB --type=ansible
在roles/nginxlb/templates中添加模板文件nginx-deployment.yaml.j2、nginx-svc.yaml.j2、nginx-cm.yaml.j2及nginx-route.yaml.j2nginx-deployment.yaml.j2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 apiVersion: v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: nginxlb: {{ meta.name }} app: {{ meta.name }} name: {{ meta.name }} namespace: {{ meta.namespace }} spec: replicas: {{ size }} selector: matchLabels: nginxlb: {{ meta.name }} template: metadata: labels: nginxlb: {{ meta.name }} spec: containers: - image: "{{ nginx_image | default('docker.io/xhuaustc/nginx:alpine') }} " name: nginx volumeMounts: - mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf name: nginx-config-hgj4i subPath: nginx.conf readOnly: true volumes: - configMap: defaultMode: 420 name: nginx items: - key: nginx.conf path: nginx.conf name: nginx-config-hgj4i
nginx-svc.yaml.j2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: {{ meta.name }}-{{ item.port }}-nginx-service namespace: {{ meta.namespace }} spec: ports: - name: {{ item.protocol | lower }}-{{ item.port | lower }} port: {{ item.port }} {% if item.protocol == 'HTTP' % } protocol: TCP {% else % } protocol: {{ item.protocol }} {% endif % } {% if item.nodeport is defined % } nodePort: {{ item.nodeport }} {% endif % } selector: nginxlb: {{ meta.name }} {% if item.nodeport is defined % } type: NodePort {% else % } type: ClusterIP {% endif % }
nginx-cm.yaml.j2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: nginx namespace: {{ meta.namespace }} data: nginx.conf: | worker_processes 1; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024 ; } stream{ {% for lb in loadbalancers % } {% if lb.protocol in ["TCP" , "UDP" ] % } upstream {{meta.name }}-{{lb.protocol}}-{{lb.port}}{ {% for upstream in lb.upstreams % } server {{upstream }}; {% endfor % } } server { {% if lb.protocol in ["UDP" ] % } listen {{lb.port }} udp; {% else % } listen {{lb.port }}; {% endif % } proxy_pass {{meta.name }}-{{lb.protocol}} -{{lb.port}} ; } {% endif % } {% endfor % } } http { include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"' ; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65 ; gzip on; {% for lb in loadbalancers % } {% if lb.protocol in ["HTTP" ] % } upstream {{meta.name }}-{{lb.protocol}} -{{lb.port}} { {% for upstream in lb.upstreams % } server {{upstream }}; {% endfor % } } server { listen {{lb.port }}; location / { proxy_pass http://{{meta.name}} -{{lb.protocol}} -{{lb.port}} ; } } {% endif % } {% endfor % } }
nginx-route.yaml.j2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 apiVersion: route.openshift.io/v1 kind: Route metadata: name: {{ meta.name }}-{{ item.port }}-nginx-route namespace: {{ meta.namespace }} spec: host: "{{ item.hostname }} " port: targetPort: {{ item.protocol | lower }}-{{ item.port | lower }} to: kind: Service name: {{ meta.name }}-{{ item.port }}-nginx-service
在roles/nginxlb/tasks/main.yaml中添加执行任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 --- - name: create nginx configmap k8s: state: present definition: "{{ lookup('template', 'nginx-cm.yaml.j2') | from_yaml }} " - name: create nginx DeploymentConfig k8s: state: present definition: "{{ lookup('template', 'nginx-dc.yaml.j2') | from_yaml }} " - name: create nginx service k8s: state: present definition: "{{ lookup('template', 'nginx-svc.yaml.j2') | from_yaml }} " with_items: "{{ loadbalancers }} " - name: create nginx route k8s: state: present definition: "{{ lookup('template', 'nginx-route.yaml.j2') | from_yaml }} " when: item.hostname is defined with_items: "{{ loadbalancers }} "
构建nginx-lb operator镜像,并推送到镜像仓库
1 2 $ operator-sdk build docker.io/xhuaustc/nginxlb-operator:v0.0.1 $ docker push docker.io/xhuaustc/nginxlb-operator:v0.0.1
operator-sdk默认是只能在operator应用所在的namespace下创建资源,如果需要在集群下全局的namespace都能使用NginxLB资源,需要对deploy/operator.yaml作修改。
将WATCH_NAMESPACE值设置为””
更新为步骤4中构建的镜像
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginxlb-operator spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: name: nginxlb-operator template: metadata: labels: name: nginxlb-operator spec: serviceAccountName: nginxlb-operator containers: - name: ansible command: - /usr/local/bin/ao-logs - /tmp/ansible-operator/runner - stdout image: "docker.io/xhuaustc/nginxlb-operator:v0.0.1" imagePullPolicy: "Always" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /tmp/ansible-operator/runner name: runner readOnly: true - name: operator image: "docker.io/xhuaustc/nginxlb-operator:v0.0.1" imagePullPolicy: "Always" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /tmp/ansible-operator/runner name: runner env: - name: WATCH_NAMESPACE value: "" - name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name - name: OPERATOR_NAME value: "nginxlb-operator" volumes: - name: runner emptyDir: {}
更新deploy/role.yaml与deploy/role_binding.yaml
role.yaml与role_binding.yaml中的kind: Role更新为kind: ClusterRole
role_binding.yaml中的kind: RoleBinding更新为kind: ClusterRoleBinding
添加额外的权限,如route资源类型的权限等role.yaml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: nginxlb-operator rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods - services - endpoints - persistentvolumeclaims - events - configmaps - secrets verbs: - '*' - apiGroups: - apps resources: - deployments - daemonsets - replicasets - statefulsets verbs: - '*' - apiGroups: - extensions resources: - deployments - daemonsets - replicasets - statefulsets - deployments/finalizers verbs: - '*' - apiGroups: - route.openshift.io attributeRestrictions: null resources: - '*' verbs: - '*' - apiGroups: - monitoring.coreos.com resources: - servicemonitors verbs: - get - create - apiGroups: - apps resourceNames: - nginxlb-operator resources: - deployments/finalizers verbs: - update - apiGroups: - fcloudy.com resources: - '*' verbs: - '*'
role_binding.yaml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: nginxlb-operator subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: nginxlb-operator namespace: nginxlb-operator roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: nginxlb-operator apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
至此完成了NginxLB Operator的制作,制作的结果输出为:
Operator镜像:docker.io/xhuaustc/nginxlb-operator:v0.0.1
deploy中的yaml配置文件:
测试验证
创建nginxlb-operator项目
1 [root@master ~]# oc new-project nginxlb-operator --display=NginxLBOperator
部署nginxlb-operator
1 2 [root@master ~]# oc create -f deploy/crds/fcloudy_v1alpha1_nginxlb_crd.yaml [root@master ~]# oc create -f deploy/
查看nginxlb-operator运行状态
1 2 3 [root@master ~]# oc get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginxlb-operator-85c77c8cdc-c2gpp 2/2 Running 10 1m
新建NginxLB项目
1 [root@master ~]# oc new-project nginxlb --display-name=NginxLB
使用NginxLB创建负载均衡器Nginx应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@master ~]# cat << EOF | oc create -f - apiVersion: fcloudy.com/v1alpha1 kind: NginxLB metadata: name: example-nginxlb spec: size: 2 loadbalancers: - nodeport: 32289 port: 8123 protocol: TCP upstreams: - 192.168.4.5:123 - 192.168.5.3:123 - hostname: xx.nginx.fcloudy.com port: 8080 protocol: HTTP upstreams: - 192.168.4.5:80 EOF
查看NginxLB资源状态
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 [root@master ~]# oc get all NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/example-nginxlb-6788db776-42rsz 1/1 Running 0 5s pod/example-nginxlb-6788db776-8cxm9 1/1 Running 0 5s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/example-nginxlb-8080-nginx-service ClusterIP 172.30.167.107 <none> 8080/TCP 2s service/example-nginxlb-8123-nginx-service NodePort 172.30.108.138 <none> 8123:32289/TCP 3s NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/example-nginxlb 2 2 2 2 5s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/example-nginxlb-6788db776 2 2 2 5s NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD route.route.openshift.io/example-nginxlb-8080-nginx-route xx.nginx.fcloudy.com example-nginxlb-8080-nginx-service http-8080 None
更新NginxLB example-nginxlb,将size更新为1,只使用一个Nginx应用副本
1 2 3 4 5 [root@master ~]# oc patch NginxLB example-nginxlb -p '{"spec":{"size":1}}' --type=merge nginxlb.mbcloud.com/example-nginxlb patched [root@master ~]# oc get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE example-nginxlb-6788db776-8cxm9 1/1 Running 0 2m
总结
以上实例只是对一种CRD进行控制与管理,其实一个Operator可以同时管理与控制多个CRD。
Operator能够非常灵活地实现对资源的重新管理及控制,方便对应用生命周期管理。
使用Operator-sdk,我们可以轻松创建自己的Operator。
参考文章https://www.openshift.com/learn/topics/operators https://coreos.com/operators/